An Operation Can Reduce the Likelihood of Biological Contamination by
Footstep 2: Evaluate the risks
In this section, larn how to respond these questions:
- How probable is a risk and how severe is information technology?
- Is the risk acceptable or unacceptable?
a. Characterize the risks
There are various and multiple risks involved in performing laboratory testing. The risk assessment should evaluate each risk against a standard set of criteria so that the assessed risks can be compared confronting each other. The criteria should focus on both the likelihood of the undesirable incidents occurring and the consequences if those undesirable incidents were to occur.
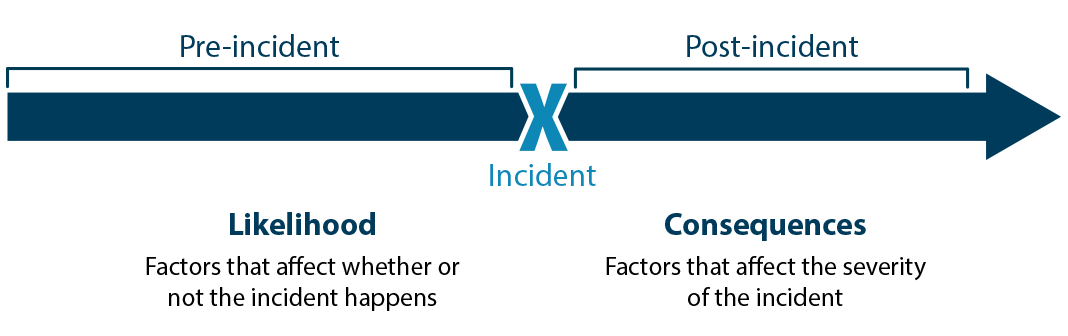
Source: Sandia National Laboratory Biosafety and Biosecurity Adventure Assessment Technical Guidance Certificate, 2014.
Likelihood and Consequences of Risk
The likelihood component of risk includes factors that touch whether or not the incident happens and occurs before the actual incident occurs; the consequences of adventure considers factors that affect the severity of an incident after information technology has occurred.
It is important to define what is being evaluated considering some factors tin affect the likelihood and consequences. For example, the availability of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) tin reduce the likelihood of exposure merely wearing the appropriate PPE correctly can also reduce the consequences if an exposure occurs.
Likelihood of Chance
Some factors to consider that tin can affect the likelihood of an undesirable incident (such equally exposure to a biological agent in this example) include:
- Biological amanuensis factors
- Stability in the environment (e.one thousand., ability to produce spores, resistance to disinfectants)
- Potential routes of transmission (direct mucosal contact, inhalation, ingestion, injection)
- Endemicity of biological agent in the local environment and population (east.g., owned or exotic) and host range
- Life stage/course of the biological amanuensis (e.g., dimorphic fungi, antigenic shift)
- Communicability
- Laboratory/testing environment factors
- Concrete infrastructure and existing controls: the type of facility, presence of engineering/condom controls, blazon of equipment used, function/reliability of ventilation systems
- Procedural: existence of administrative controls such as policies and training; availability of appropriate PPE; generation of aerosols and apply of sharps; amplification of the biological agent by culturing, and the types and complication of procedures beingness conducted
- Homo factors
- Competency of personnel, level of grooming
- Behavioral aspects
- Stress, gamble perception, take chances tolerance
- Post-obit condom piece of work practices
To evaluate the consequences after an undesirable incident occurs, appraise the characteristics of the hazard(southward) or biological agents, the health and immune status of the laboratory/testing personnel, and the availability of vaccines, prophylaxis, or therapies.
Consequences of Risk
Some factors to consider that can touch on the consequences of an undesirable incident (such as infection in this example) include:
- Biological amanuensis factors
- Virulence factors: adhesion, invasiveness, toxigenesis, production of exoenzymes, antigenic variation, resistance to antibiotics, tissue tropism, multiple replication sites inside-host, ability to arm-twist autoantibodies against host)
- High communicability
- Severity of infection/affliction (morbidity/mortality rate)
- Infectious dose
- Administrative controls
- Availability of vaccines, prophylaxis, therapeutic interventions, and emergency response procedures
- Host factors
- Health and immune status of staff: immunocompetent or immunocompromised, pregnancy, pre-existing medical conditions, allergies, age, large susceptible population
- Behavioral aspects
- Willingness to accept vaccines
- Adherence to safe piece of work practices and proper utilise of PPE
b. Prioritize the risks and determine if risks are acceptable
Information technology is important to acknowledge that risks tin exist reduced, but by and large cannot be completely eliminated unless the piece of work is discontinued entirely (eastward.chiliad., elimination) or modified to incorporate less harmful activities such as using surrogates (e.g., substitution).
The risk assessment team should utilize the results to determine which risks are relatively college or lower than other risks. Based on the risk cess, the institution/testing site should decide which risks are adequate (work tin can proceed with the existing controls), and which risks are unacceptable (work cannot proceed until additional mitigation controls are implemented to reduce the risk to an acceptable level).
petherickacketwound.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.cdc.gov/safelabs/resources-tools/bio-risk-assessment.html
0 Response to "An Operation Can Reduce the Likelihood of Biological Contamination by"
Post a Comment